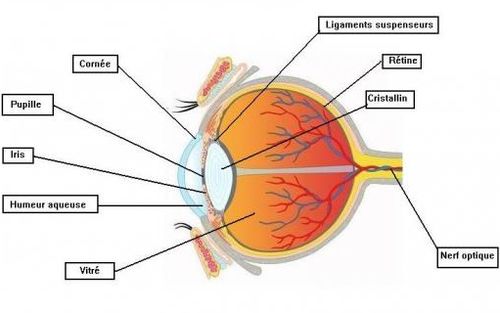
Anatomy of the eye
 The eye is a complex organ made up of a large number of items each with a specific function.
The eye is a complex organ made up of a large number of items each with a specific function.
Knowledge of the anatomy of the eye and the role of each of the elements that compose to understanding eye conditions.
Schematic section of the eye
the Cornea
The cornea is a transparent membrane at the surface of the eye. This is a lens providing the refraction of light rays towards the inside of the eye.
The secretion of tears and regular eyelid blink allow the membrane to constantly stay clean.
the Lens
The lens is a biconvex lens, located behind the pupil, which converges the light rays on the retina.
It allows the accommodation phenomenon, that is to say to obtain a sharp image regardless of the distance at which the observed object is located.
This "tuning" is possible due to the deformability of the lens: Indeed, this "soft lens" is attached to the inner wall of the eyeball by the ciliary muscles. According to these muscles are tense or at rest, crystalline bomb (making net objects seen in the distance) or remains flat (allowing observation of nearly)
The Iris
The iris is the colored part of the eye.
This is a ring-shaped muscle that delimits the pupil.
Located in front of the lens, he plays the role of a “diaphragm” which reacts to changes in light intensity:
– When the light is strong, the iris contracts and reduces the light intensity that strikes the retina, avoiding blinding.
– On the contrary, when the light intensity is low, iris opens to let in the most light possible.
The retina
The retina contains nerve cells called photoreceptors specialized.
Located at the back of the eye, it constitutes the "screen" which receives the image formed by the cornea and lens. It transforms the image into electric signals and transmits to the brain via the optic nerve.
Vitreous Humor
The vitreous or vitreous humor is a gelatinous and transparent body that holds the retina against the wall of the eye.
Aqueous Humor
Aqueous humor is a clear fluid that brings oxygen and nutrients to the lens and the cornea.
The Optic Nerve
The optic nerve leading to the brain sensory information gathered by the photoreceptors of the retina.