Cheyletiellose and demodectic mange
Here is a presentation of two lesser known skin parasites :
.
The Cheyletiellose
.
Presentation
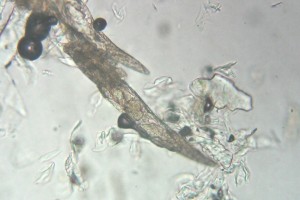
Cheyletiella is a mite of large feeding on scales on the skin of animals, including dogs and rabbits. Females lay eggs on hair. The complete cycle lasts 3 about weeks. The cheyletielles can survive 5 to 6 weeks in the external environment, They then feed of small dust mites, but need a host to reproduce.
The source of parasites is in adult dogs which can remain carriers and the external environment healthy.
It is a common pathology in community, most often seen in young animals, but also on adults weakened by other pathologies.
It's a contagious to humans, which then shows papules, small scabs and itching, mainly on the arms, legs or trunk. These lesions regress spontaneously when the animal is processed.
.
Clinic
Affected animals itch much, have many dander (dandruff) of different sizes, localized or diffuse depilations, Erythema, papules, crusts, mainly on the back line.
.
Treatment
For the treatment, used of spot - we used classically flea, but at intervals of 2 weeks. It is very important to treat all the animals in the presence, in order to avoid recontamination.
In community, the parasite is most difficult to eradicate. We must treat the environment and proceed to crawl from 2 to 3 weeks.
.
The demodectic mange
.
Presentation
Demodex is a parasite to multiply in the hair follicles and sebaceous glands of animals, in immune deficiency of hereditary origin in the young, or secondary to a general pathology in adults. Mothers giving birth to puppies demodeciques should be removed from the breeding.
It feeds exclusively on sebum, and cannot survive in the external environment. Its life cycle is 10 to 12 days and takes place entirely in the hair follicle and sebaceous glands.
50 % adult dogs are carrying this parasite healthy. It is spread from the mother to her puppies during the neonatal period. The clinical form will develop in immunodeficiency.
.
Clinic
The symptoms are extremely varied, What makes diagnosis difficult.
There are localized forms, posing by rather round depilations, erythematous and squamous, most often on the face (eyelids and lips), the limbs and trunk are less frequently affected. These lesions will regress spontaneously in a few weeks in 90% cases. Ras-haired dogs are frequently concerned.
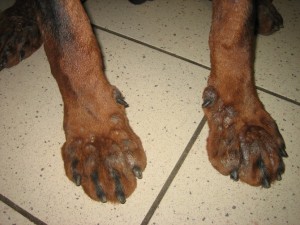
The podales forms are more serious, characterized by erythematous swelling, painful around the nails, between the fingers. They can be complicated to superinfection, with boils, or ulcers.
The generalized form is at least 5 distinct zones, one area of the body as a whole, or several ends podales. The lesions are highly variable : depilations, Erythema, dander, comedones, and get complicated frequently bacterial infection that may be deep.
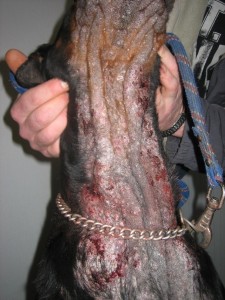
Pyodemodecie
The only way to visualize this parasite is to perform skin scrapings to examine them under the microscope.
.
Treatment
The treatment is still long (several months), expensive. It is put in place when the forms generalized or surinfectees.
There are different forms of treatment, dermal or oral, adapted to each animal. It not only stopped when 2 skin scrapings are negative at one month apart. Then, regular monitoring is essential, because there are relapses in 15 % cases.
.